Google Releases Open-Source Watermarking Tool for Text Generated by AI
Most people like
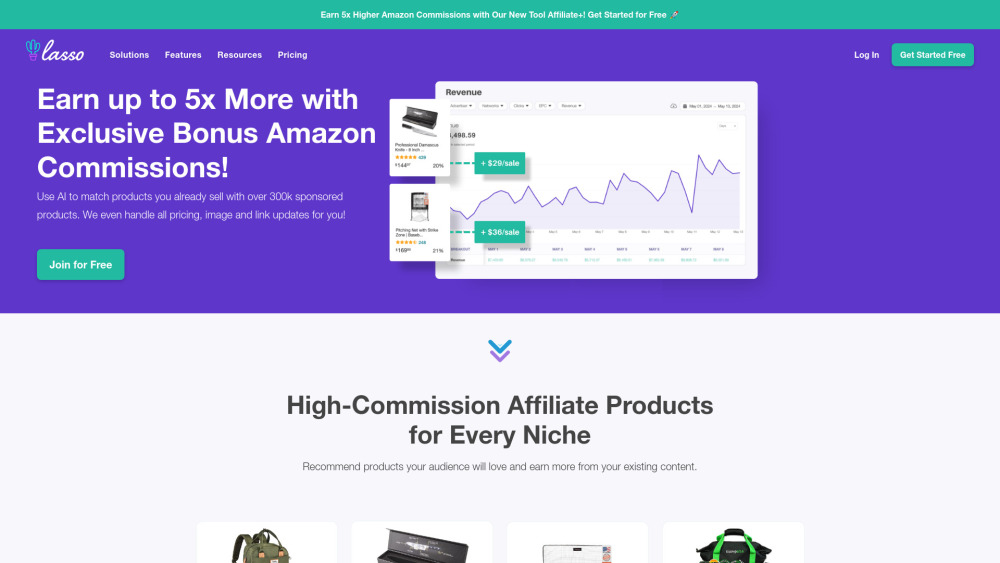
Welcome to our AI-driven affiliate marketing platform, where innovation meets opportunity. Our cutting-edge technology empowers businesses and marketers to optimize their affiliate strategies, driving sales and boosting engagement. By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, we analyze data in real-time, enabling targeted campaigns that convert. Whether you're a seasoned marketer or new to affiliate marketing, our platform offers the tools and insights you need to maximize your success in the digital marketplace. Discover how our AI-driven solutions can transform your affiliate marketing efforts today!

Discover a groundbreaking AI-driven tool designed to enhance students' writing skills and boost academic success.
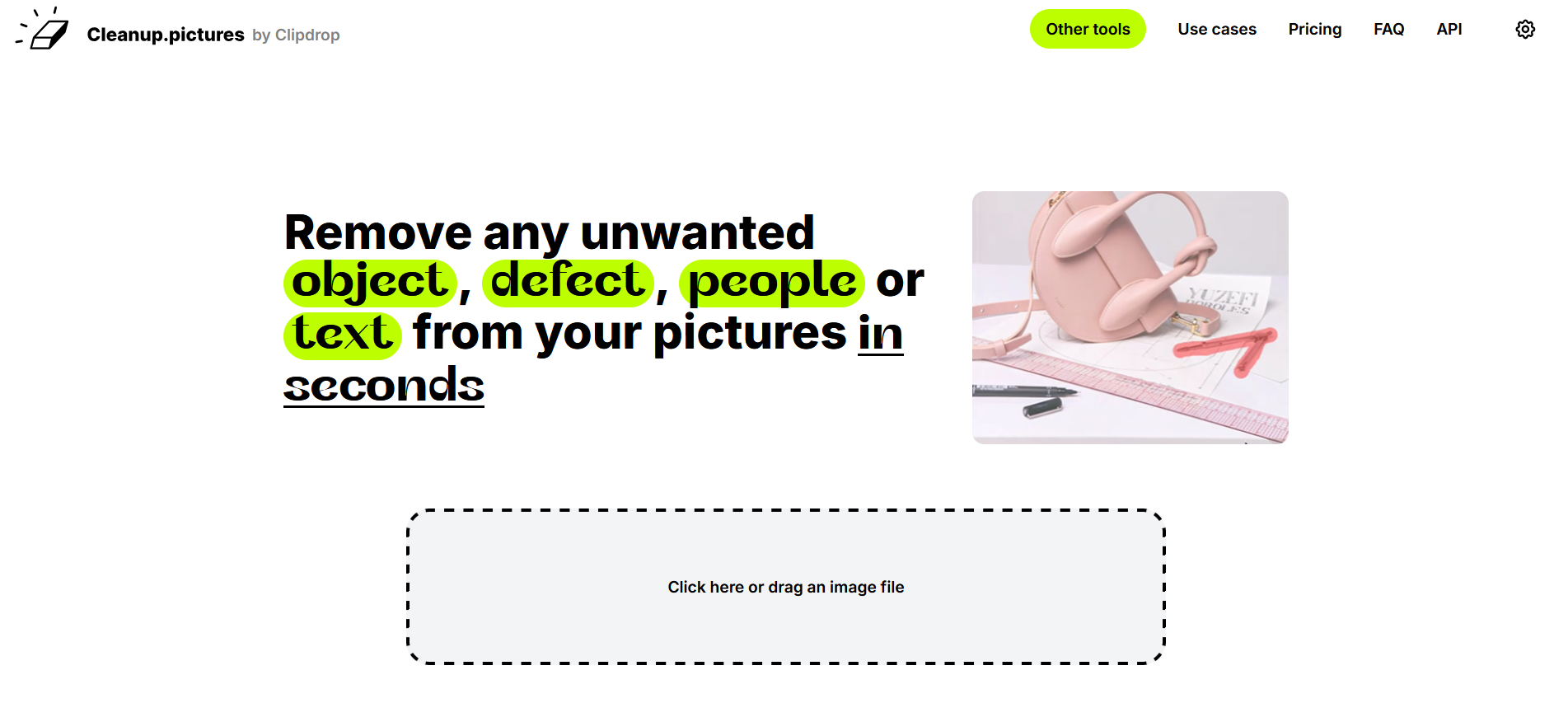
Cleanup.pictures is a free web app that lets users remove objects, people, text, and defects from any image.
Find AI tools in YBX
Related Articles
Refresh Articles

