Is Generative AI Just a Temporary Hype? DeepMind's Founder Discusses the Future of Interactive AI and Its Path to Freedom
Most people like
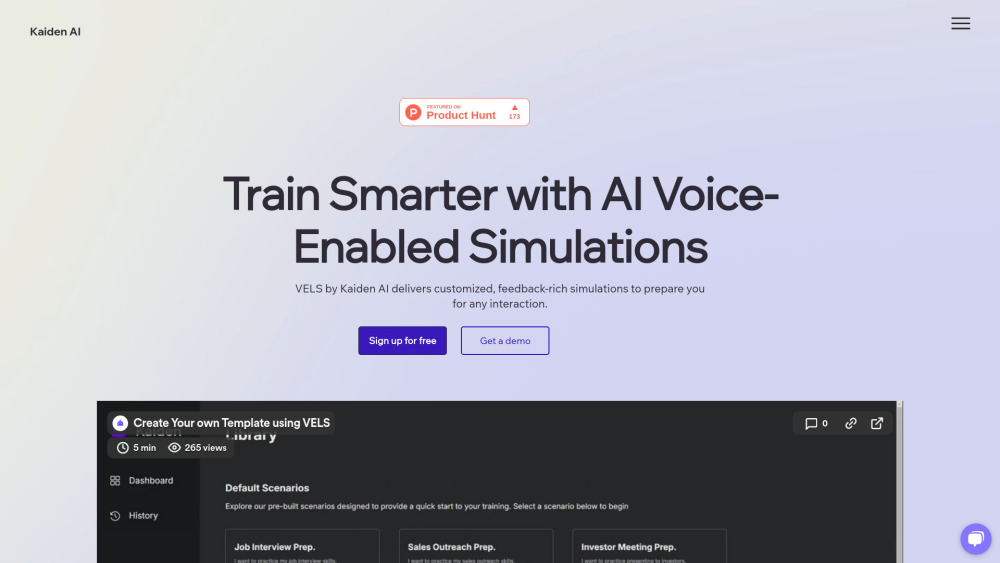
Harnessing AI Voice Simulations for Enhanced Professional Skills Training
In today's rapidly evolving workplace, effective communication and specialized skills are paramount. AI voice simulations are revolutionizing professional skills training by providing immersive and realistic practice experiences. These advanced tools are designed to enhance learning outcomes, improve confidence, and foster the development of essential competencies across various industries. Discover how AI voice simulations can transform your professional training initiatives and prepare you for success in a competitive job market.
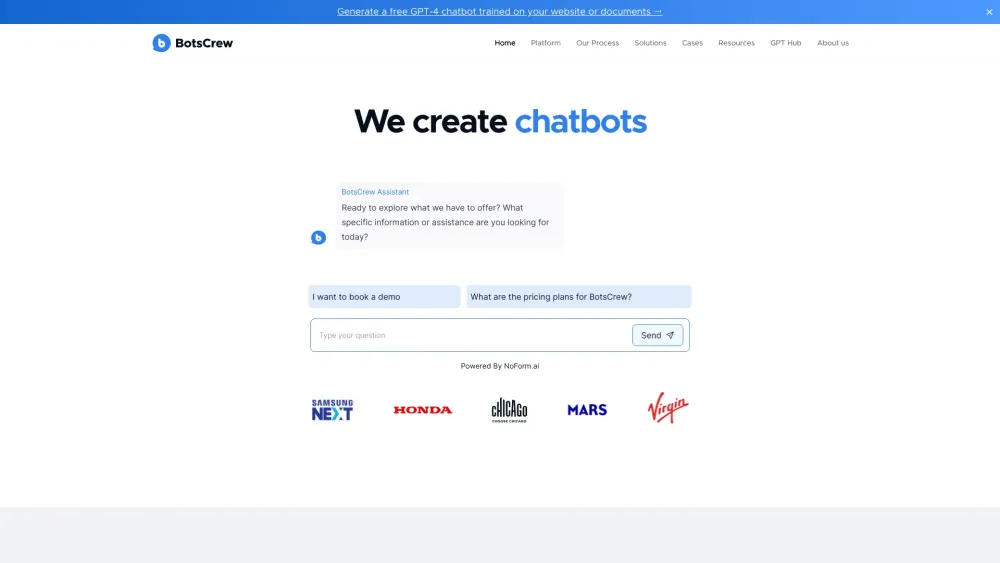
In today's digital landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to smart custom chatbots to enhance customer interactions and streamline operations. By leveraging advanced AI technology, these chatbots can provide personalized support, answer queries in real-time, and significantly improve user experiences. Whether you're looking to boost sales, improve customer service, or automate repetitive tasks, investing in custom chatbot development is a strategic move for any forward-thinking organization. Explore the transformative potential of chatbots and how they can drive growth and engagement for your brand.
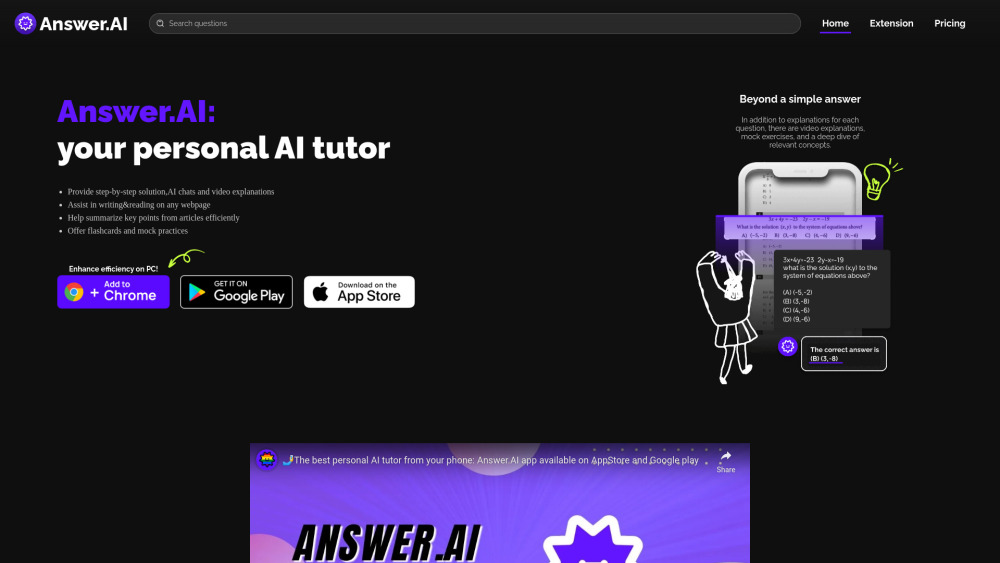
Unlock the potential of your academic journey with our innovative AI-powered homework helper app. Designed to assist students in mastering complex subjects, this tool offers personalized guidance and instant support for any homework challenges. Whether you're grappling with math problems or exploring literature, our app simplifies learning with tailored resources at your fingertips. Experience the future of education and enhance your study sessions today!
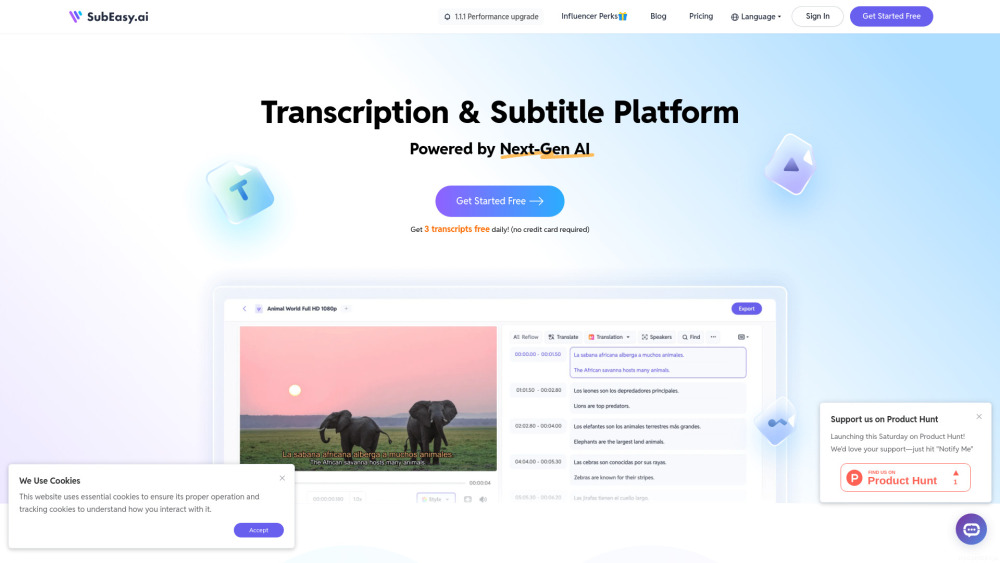
Transform your audio and video content with our advanced AI transcription and translation services. Whether you need accurate transcriptions for clarity or translations to reach a broader audience, our cutting-edge technology ensures swift and reliable results. Elevate your media with seamless accessibility and understanding today!
Find AI tools in YBX
Related Articles
Refresh Articles
