Stanford AI Identifies Nearly Every Solar Panel Installed in the U.S.
Most people like

Discover the ultimate all-in-one money management platform designed to drive your financial growth and success.
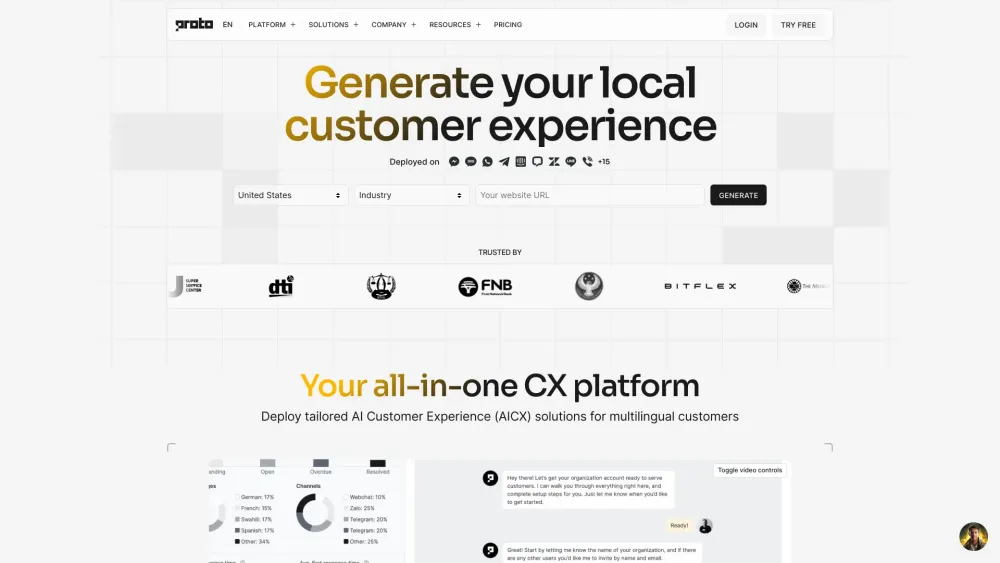
Discover the power of inclusive customer experience (CX) automation and the benefits of multilingual contact center automation. Leverage innovative solutions to enhance engagement, streamline communication, and cater to diverse audiences. Transform your customer interactions by embracing technology that prioritizes inclusivity and linguistic diversity.
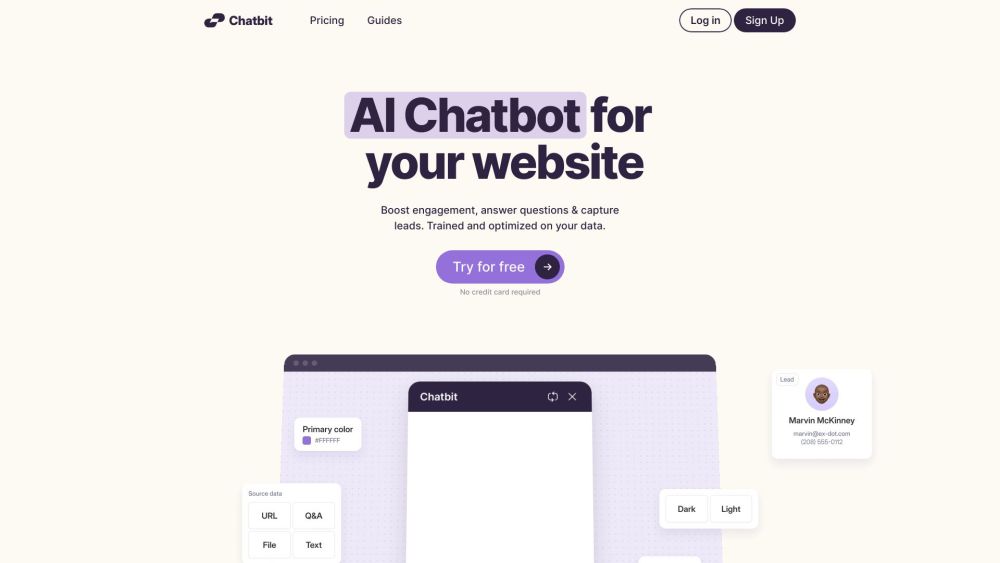
Elevate your customer interactions with custom AI chatbots tailored to your unique data. These intelligent virtual assistants are designed to enhance engagement and deliver personalized experiences, ensuring your business stands out in the digital landscape. Discover the power of AI chatbots specifically trained to meet your needs.
Discover the power of AI image generators that transform text prompts into stunning visuals. With cutting-edge technology, these tools allow users to convert imaginative descriptions into captivating images, bridging creativity and innovation effortlessly. Unlock your artistic potential and explore the limitless possibilities of AI-driven imagery!
Find AI tools in YBX
Related Articles
Refresh Articles
