Understanding Margins: Cohere Founder Discusses Rapid Changes in AI Business Models
Most people like
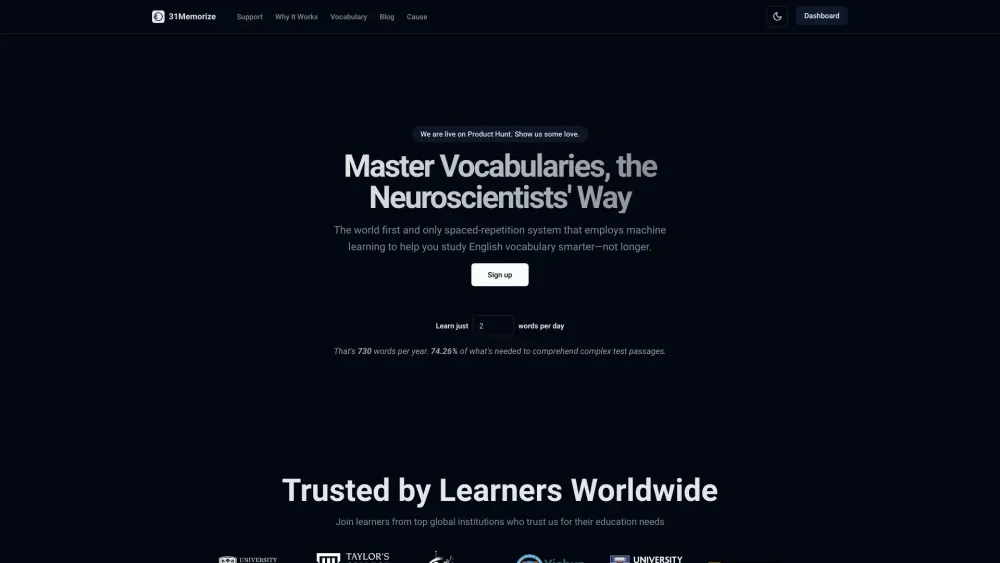
Enhance Your English Vocabulary with Smart Learning Techniques
Unlock the power of effective English vocabulary learning with innovative strategies tailored to boost your language skills. By employing smart techniques, you can expand your vocabulary efficiently and confidently. Discover how to optimize your learning experience while mastering the nuances of the English language.
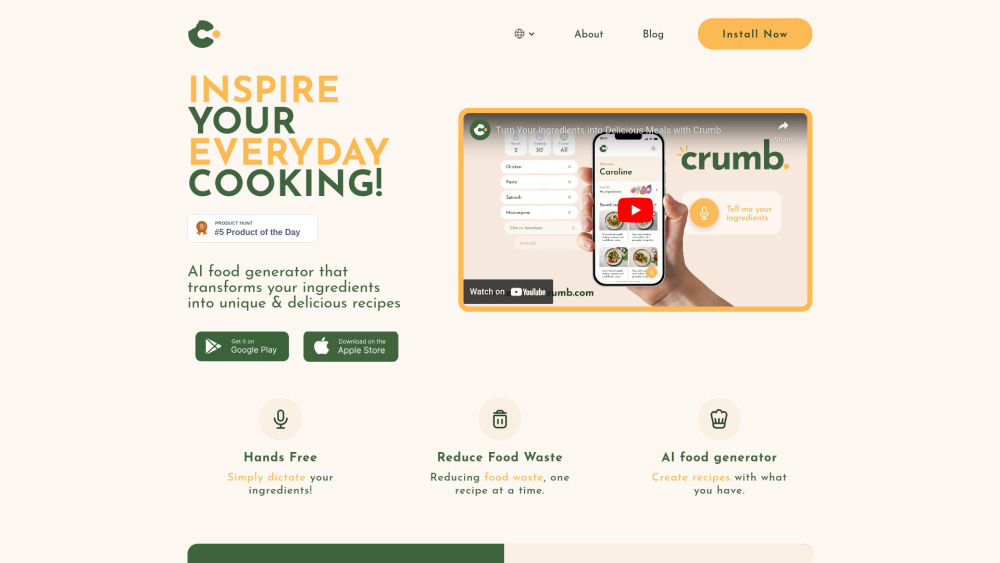
Discover our AI recipe generator that crafts unique dishes tailored to the ingredients you have on hand. Unleash culinary creativity and transform your pantry into a gourmet kitchen with personalized recipes at your fingertips!
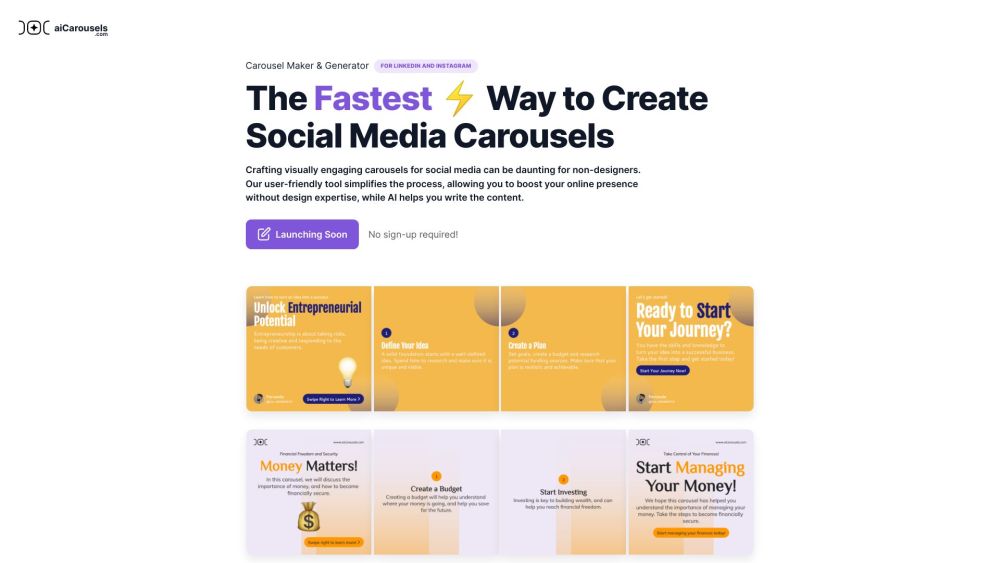
Easily craft stunning carousels for your social media platforms with aiCarousels.com. Our user-friendly tool empowers you to engage your audience and enhance your online presence.
Explore the ultimate travel guides and product reviews hub! Our platform is designed for adventurers and savvy shoppers alike, offering in-depth insights on top destinations and must-have items. Whether you're planning your next getaway or searching for the best gear, we provide you with reliable information and expert reviews to elevate your experience. Join us in discovering the world, one guide and review at a time!
Find AI tools in YBX
Related Articles
Refresh Articles
