Unleashing GPT-4: Stunning Performance in Ophthalmic Evaluation and Expert Recommendations for Cautious Implementation
Most people like
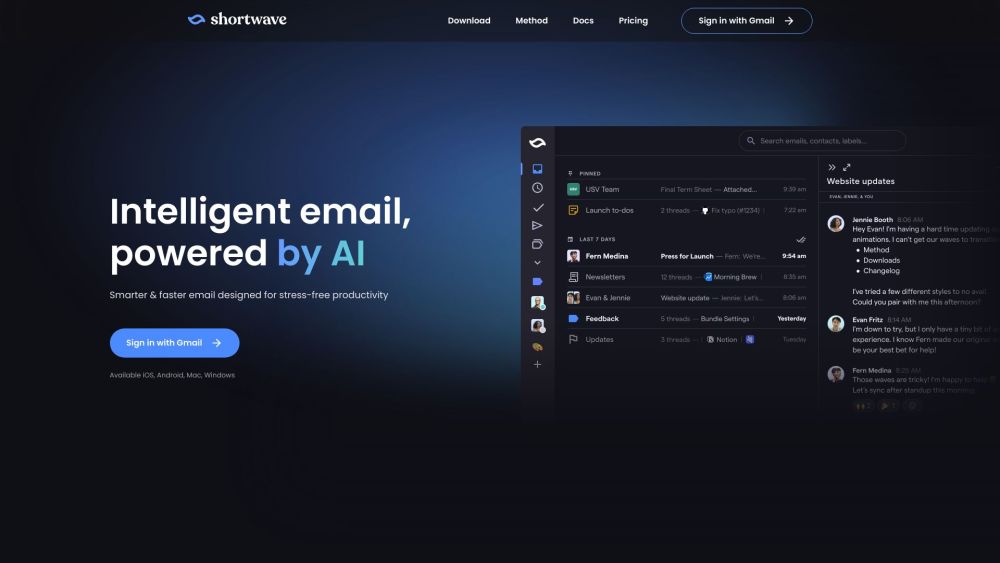
Shortwave is an AI-driven email service designed specifically for professionals to enhance productivity and eliminate stress.
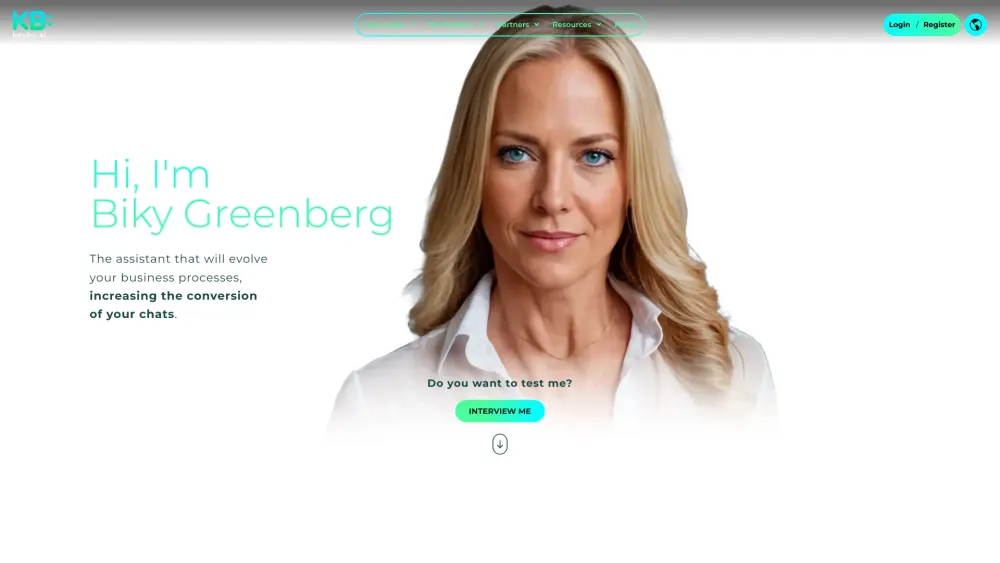
Enhance Your Sales Performance with KB: Smart Chat
Unlock the potential of your sales team and drive results with KB: Smart Chat. This powerful tool is designed to elevate your customer interactions and streamline the communication process, ultimately leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction. Discover how leveraging KB: Smart Chat can transform your sales strategy and fuel your business growth today!
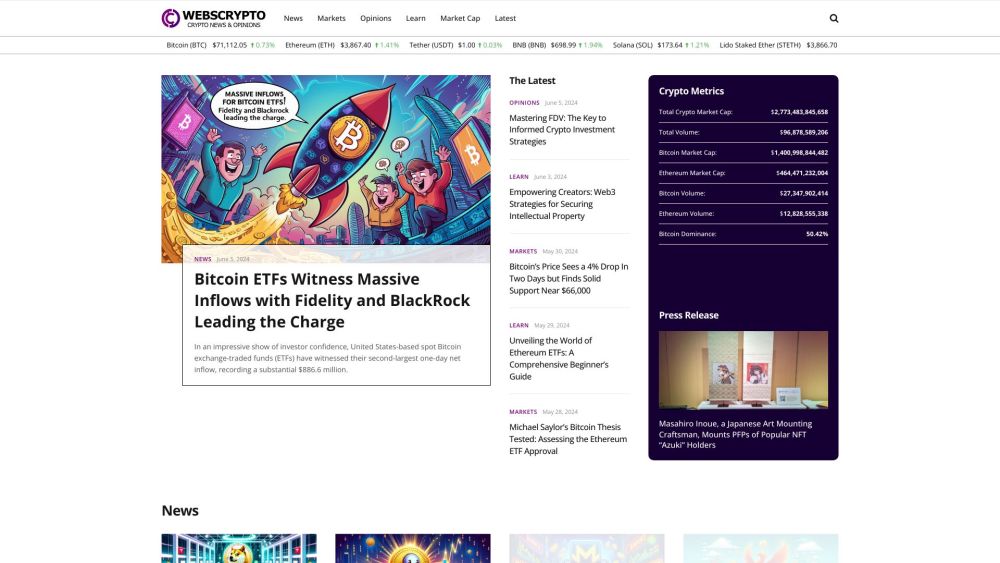
Welcome to your go-to source for the latest in cryptocurrency news! Stay informed with real-time updates, expert insights, and in-depth analysis of the ever-evolving crypto landscape. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, our hub provides valuable information to help you navigate the dynamic world of digital currencies. Keep up with trends, market movements, and technological advancements that shape the future of finance. Dive in and explore the exciting realm of crypto today!
Discover the transformative potential of an AI-powered content writing platform designed to enhance your writing process. By leveraging advanced artificial intelligence, this innovative tool streamlines content creation, allowing you to produce high-quality articles, blog posts, and marketing copy effortlessly. Whether you're a seasoned writer or a busy professional, this platform empowers you to generate engaging content quickly while maintaining your unique voice. Elevate your writing experience today with the latest in AI technology!
Find AI tools in YBX
Related Articles
Refresh Articles
