IBM's 2024 Predictions: How Generative AI is Reshaping Cyberattack Strategies
Most people like
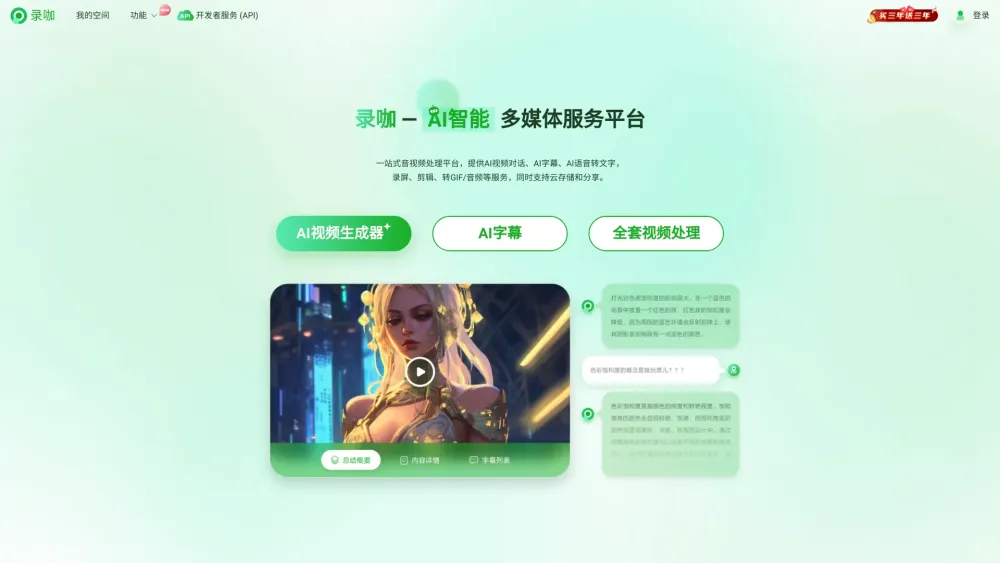
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, audio and video processing platforms are transforming the content creation field in unprecedented ways. AI-driven tools can automate editing, enhance image quality, and optimize audio, significantly improving creators' productivity. Whether in social media, video production, or live streaming, these platforms provide users with intelligent solutions that make content creation simpler and more efficient. Explore AI-driven audio and video processing platforms to elevate your creative experience.
Synthace empowers research and development teams to effortlessly conduct experiments and gather data—all without the need for coding. This innovative platform streamlines the experimental process, making it accessible to scientists and researchers of all skill levels.

Introducing our AI-Powered Transcription and Translation Service: Revolutionizing the way you convert speech into text and translate languages effortlessly. Experience fast, accurate, and reliable results tailored to your needs, making communication seamless and efficient across various platforms. Unlock the potential of artificial intelligence to enhance your workflow and connect with a global audience like never before.

Revolutionize your study sessions with our AI tutor, designed for instant homework assistance. Get accurate answers, clarifications, and guidance on your assignments, making learning more efficient and engaging. Whether you're tackling complex math problems or researching science topics, our AI tutor is here to support you every step of the way. Experience the future of education with instant help at your fingertips.
Find AI tools in YBX


