Google's Commitment to Safeguard AIGC Tool Users from Copyright Risks
Most people like
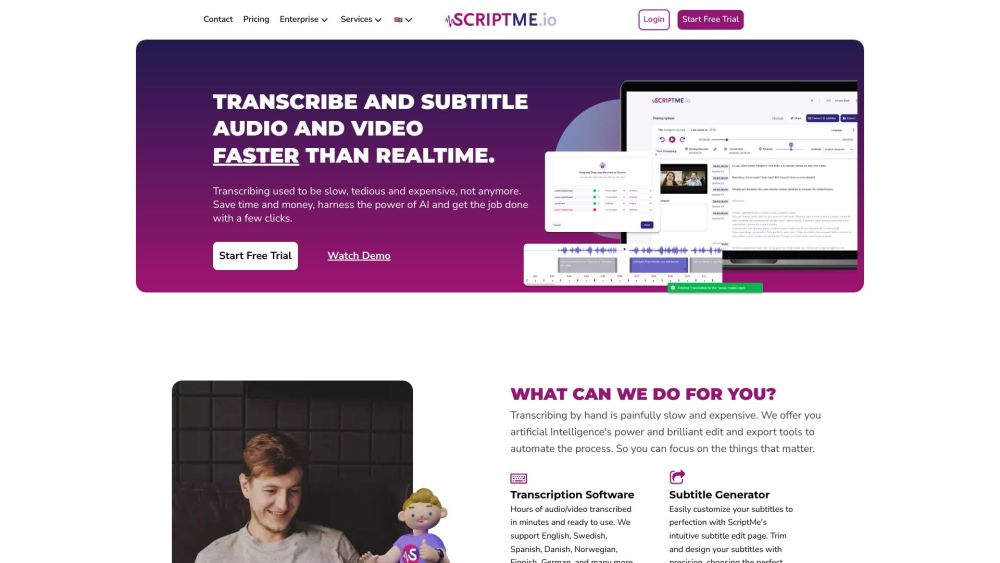
ScriptMe offers rapid and precise transcription and subtitling services in various languages, ensuring high-quality results tailored to your needs.

In today's digital landscape, voice cloning and text-to-speech technology are transforming the way we create and consume audio content. This innovative platform allows users to generate lifelike voiceovers and engaging spoken narratives with remarkable efficiency. By harnessing advanced machine learning techniques, our solution empowers creators, businesses, and educators to produce high-quality audio that captivates audiences while saving time and resources. Explore how this cutting-edge technology can elevate your content strategies and enhance communication.
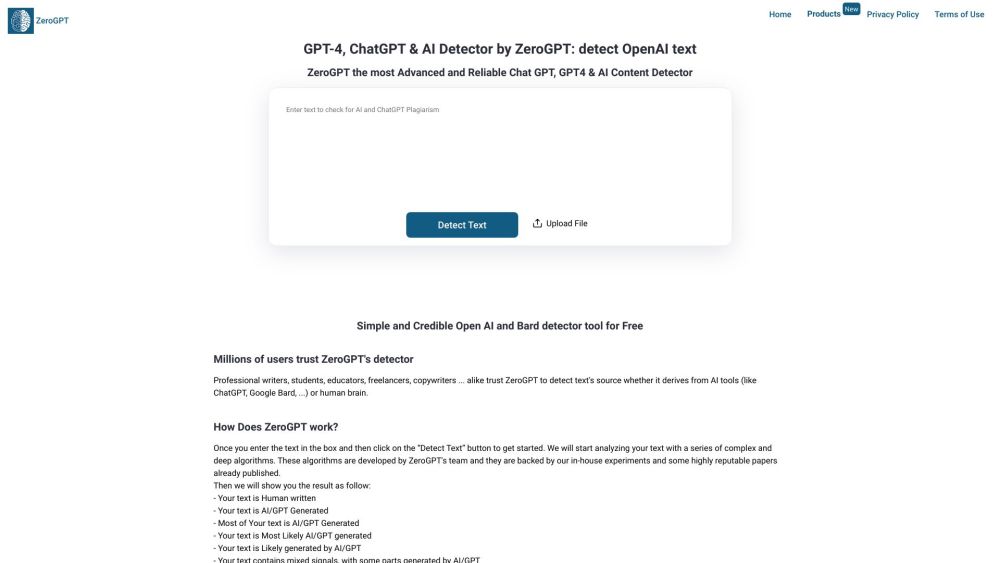
ZeroGPT is a cutting-edge AI tool designed for the accurate detection of ChatGPT content, OpenAI-generated text, and instances of plagiarism. This powerful solution provides users with reliable insights and analysis, ensuring the authenticity of written materials.
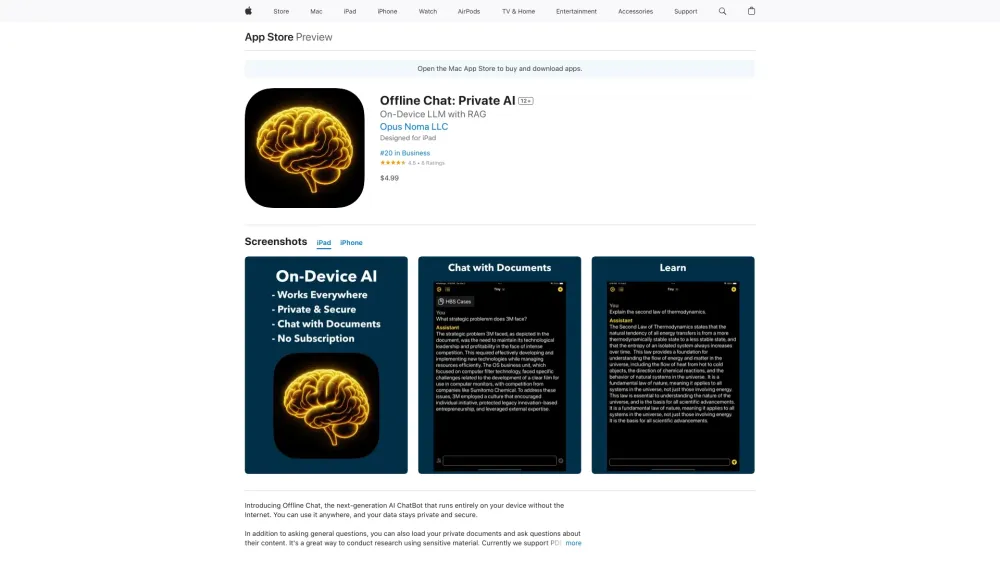
In today's digital landscape, the integration of On-Device Large Language Models (LLMs) combined with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology represents a significant breakthrough in artificial intelligence. This innovative approach not only enhances the capabilities of AI systems but also ensures that they operate efficiently at the edge, minimizing latency and maximizing performance. As we explore the intersection of on-device processing and RAG, you'll discover how this synergy transforms user experiences and drives intelligent solutions across various applications. Join us in diving deeper into this revolutionary technology!
Find AI tools in YBX
Related Articles
Refresh Articles
