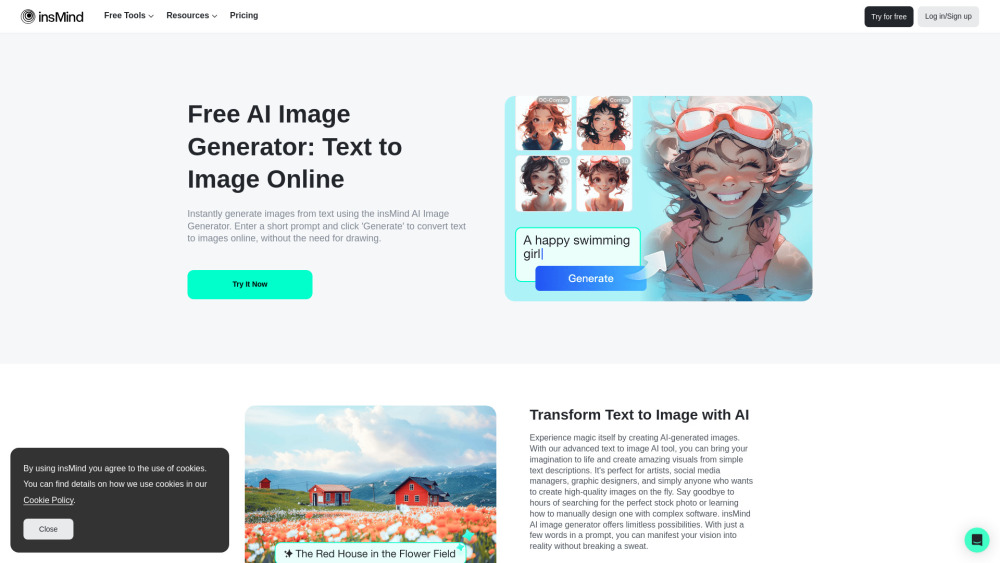
Smart Machine Learning Uncovers Eco-Friendly Chemicals for Enhanced De-Icing Solutions
Most people like

Introducing our AI-powered platform designed specifically for enterprise spend risk management. Streamline your financial oversight with advanced analytics and proactive risk mitigation, ensuring that your organization effectively manages expenditures while safeguarding against potential financial pitfalls. Enhance your decision-making processes and maximize profitability with our innovative solution tailored for today's competitive business landscape.
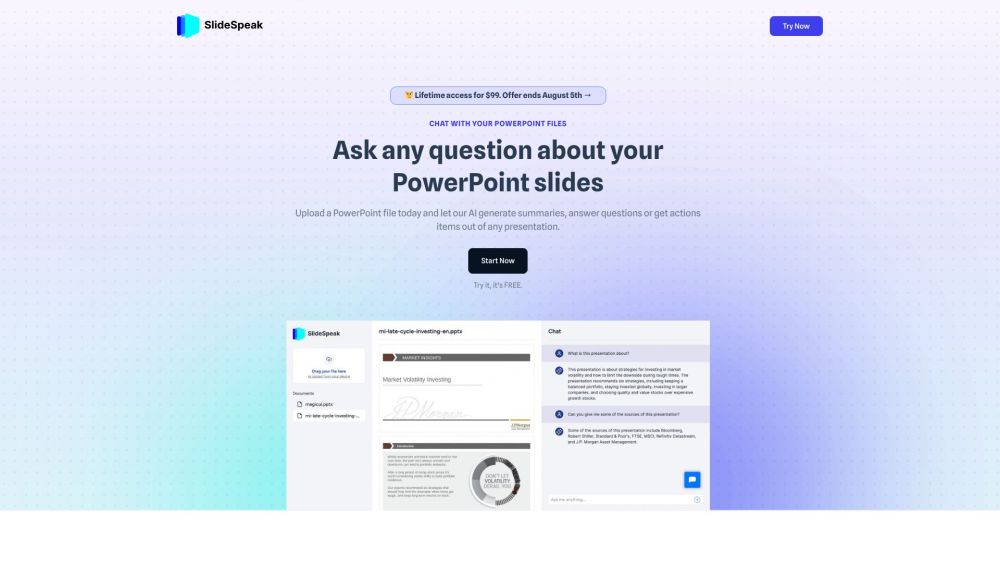
Introducing SlideSpeak, an innovative chat platform designed to enhance user engagement with PowerPoint slides. This dynamic tool enables seamless interaction, transforming the way audiences experience presentations and making your slides more interactive than ever.
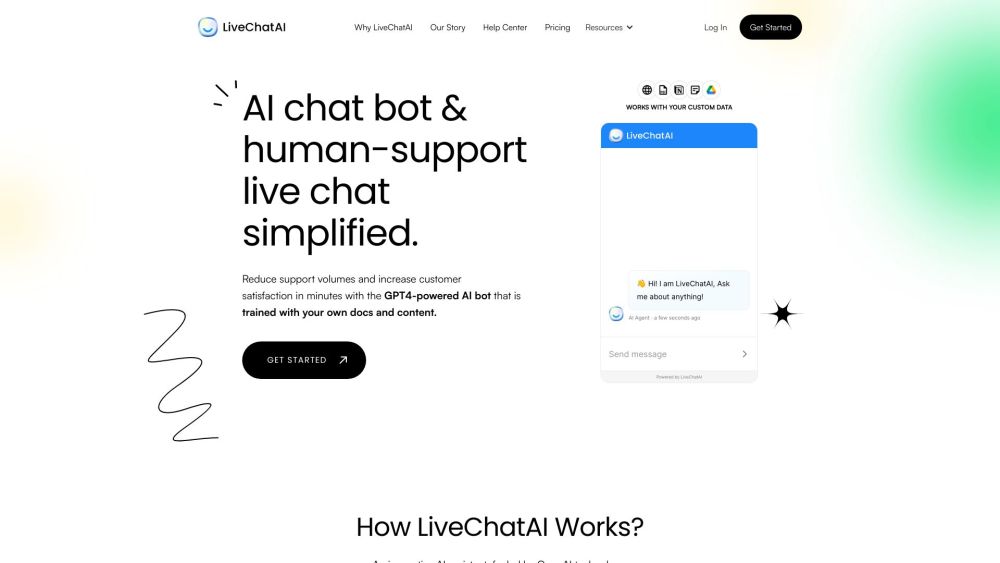
Enhance Your Customer Support Experience with AI Chatbots and Live Chat Solutions
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, delivering exceptional customer support is essential. By integrating AI chatbots alongside live chat options, businesses can streamline their customer service operations, providing instant assistance and personalized interactions that boost satisfaction and efficiency. Discover how these innovative tools can transform your support strategy and elevate your customer experience.
Find AI tools in YBX
Related Articles
Refresh Articles